Dispersive Zero Trust Academy
Practical Insights & Advanced Strategies for Building a Secure, Resilient Network
Introduction
At the Dispersive Zero Trust Academy, we provide expert-led guidance on Zero Trust security principles, helping you identify, mitigate, and respond to evolving cyber threats. Whether you're new to Zero Trust or refining your strategy, our academy equips you with the knowledge and tools needed to fortify your security posture against modern threats.
Most practitioners agree that traditional security models are no longer sufficient. The rise of cloud computing, remote work, and IoT has introduced new vulnerabilities that require a Zero Trust approach. The Dispersive Zero Trust Academy offers comprehensive training and resources to help organizations implement, optimize, and scale Zero Trust strategies.
Zero Trust Fundamentals
Explicit Verification
- Continuous Authentication and Authorization - Dispersive extends Zero Trust beyond users to every network packet, ensuring all traffic is authenticated before transmission.
- No Implicit Trust in the Network - Internal traffic is treated with the same level of scrutiny as external, using multi-path encryption to prevent unauthorized access.
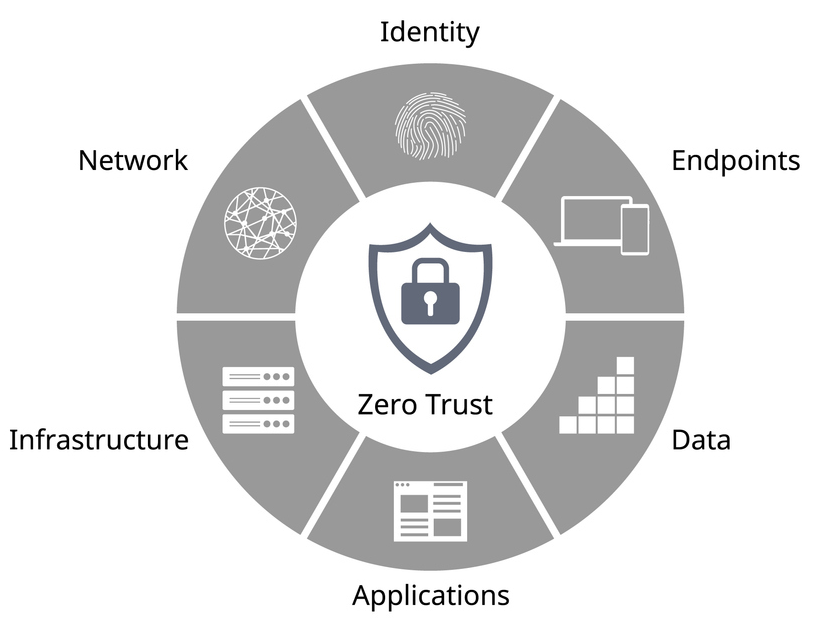
Least Privilege Access
- Micro-segmentation at the Network Layer - Isolate sensitive workloads, preventing lateral movement of threats.
- Dynamic Access Control - Real-time evaluation of users, devices, and application needs ensures granular, adaptive permissions.

Assume Breach
- Proactive Security - By dispersing data and continuously fragmenting network traffic, Dispersive makes exfiltration nearly impossible—even against quantum threats.
- Resilience & Redundancy - A multi-path architecture ensures operations remain intact, even if part of the network is compromised.

Context-Aware Access Control
- Dynamic Routing - Real-time traffic adjustments prevent unauthorized access while optimizing performance.
- AI-Powered Threat Detection - Identifies and mitigates cyber threats dynamically, rerouting traffic away from potential attacks.

Data Security
- End-to-End Encryption - Data is encrypted at every transmission point, with automatic encryption key rotation ensuring continuous protection.
- Data Dispersion - Fragmenting packets across multiple paths ensures adversaries cannot reconstruct stolen data.
Identity as the Perimeter
- Identity-Based Routing - Integrates with Okta, AD, Entra, and other identity providers to enforce strict access controls.
- Secure Remote Access - Establishes encrypted tunnels for secure remote connections, ensuring continuous verification.
Continuous Improvement
- Automated Monitoring & Adaptive Defense - AI-driven network intelligence analyzes traffic in real-time, dynamically responding to evolving threats.
- Self-Healing Network - Dispersive dynamically adjusts pathways, ensuring continuous security and reliability.
Build a Cyber-Resilient Future with Advanced Security Technologies
Anticipate and prevent attacks before they occur. Utilize advanced intelligence and machine learning to deflect emerging network infrastructure and VPN threats and proactively mitigate these risks.
- Anomaly Detection: Preemptive cyber defense technologies use machine learning algorithms to monitor network traffic and identify unusual patterns or anomalies that may indicate a potential cyber attack, allowing for swift incident response and mitigation.
- Predictive Analytics: These systems analyze large amounts of data from various sources to predict the likelihood of a cyber attack, enabling organizations to take proactive measures to strengthen their defenses and reduce the risk of successful exploitation.
- Real-time Threat Intelligence: Preemptive cyber defense technologies leverage real-time threat intelligence feeds to identify and classify known and unknown threats, providing critical insights to inform decision-making and enable swift action to protect against emerging threats.
Create a constantly changing network environment that makes it difficult for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities. Continuously modify network configurations, traffic patterns, and access controls to thwart attacks.
- Dynamic Network Partitioning: AMTD systems dynamically divide the network into multiple, isolated segments that move and reconfigure themselves in response to changing threat conditions, making it difficult for attackers to establish a foothold or maintain a connection.
- Self-Healing Network Segmentation: These systems use advanced algorithms to constantly monitor and adjust the network segmentation, ensuring that any compromised segment is quickly contained and isolated from the rest of the network, minimizing the attack surface.
- Adaptive Network Redundancy: AMTD systems automatically deploy redundant network paths and connections, making it difficult for attackers to disrupt or eliminate communication channels, while also allowing the system to rapidly recover from attacks by re-establishing new connections.
Create a constantly changing network environment that makes it difficult for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities. Continuously modify network configurations, traffic patterns, and access controls to thwart attacks.
- Dynamic Network Partitioning: AMTD systems dynamically divide the network into multiple, isolated segments that move and reconfigure themselves in response to changing threat conditions, making it difficult for attackers to establish a foothold or maintain a connection.
- Self-Healing Network Segmentation: These systems use advanced algorithms to constantly monitor and adjust the network segmentation, ensuring that any compromised segment is quickly contained and isolated from the rest of the network, minimizing the attack surface.
- Adaptive Network Redundancy: AMTD systems automatically deploy redundant network paths and connections, making it difficult for attackers to disrupt or eliminate communication channels, while also allowing the system to rapidly recover from attacks by re-establishing new connections.
Industries Ideal for Zero Trust Security
Industries that handle sensitive data and critical infrastructure are prime candidates for Zero Trust security:
- Organizations with high-security requirements
Industries like finance, healthcare, and government that handle sensitive data can benefit from the enhanced security provided by Stealth Networking. - Organizations with complex networks
Companies with multiple locations, cloud deployments, and remote workers can leverage Dispersive to secure and optimize their network infrastructure. - Organizations looking to improve network performance
The dynamic routing and multi-path technology can significantly enhance network performance and application delivery.

Best Practices for Implementing Zero Trust in Dispersed Environments
Strong Identity Foundation
- Centralized Identity and Access Management (IAM): Implement a robust IAM system to manage and authenticate users across all locations and devices. This includes strong authentication methods like multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Least Privilege Access: Strictly enforce the principle of least privilege, granting users only the minimum necessary access to perform their jobs. Regularly review and update permissions.
- Context-Aware Access Control: Implement dynamic access policies that consider user context, such as location, device posture, and time of day, to make real-time access decisions.
Secure Network Access
- Software-Defined Perimeter (SDP): Utilize SDP to create secure, encrypted connections between users and resources, regardless of their location. This isolates applications and services from the open internet. Dispersive is considered a “Software Defined Perimeter” technology.
- Micro-segmentation: Divide the network into smaller, isolated segments to limit the impact of potential breaches. This prevents lateral movement and contains attackers.
- Network Access Control (NAC): Implement NAC solutions to ensure that only authorized devices with the necessary security posture can connect to the network.

Secure Cloud and SaaS Applications
- Secure Web Gateways (SWG): Use SWGs to filter internet traffic, block malicious websites, and prevent data leakage.
- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA): Implement ZTNA to provide secure access to specific applications and resources, rather than granting access to the entire network.
Secure Endpoints
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Deploy EDR solutions to monitor endpoint activity, detect malicious behavior, and respond to security incidents.
- Mobile Device Management (MDM): Implement MDM solutions to manage and secure mobile devices, enforce security policies, and protect corporate data.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Utilize DLP tools to prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control, regardless of where it resides.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Use SIEM solutions to collect and analyze security logs from various sources, providing visibility into security events and enabling proactive threat detection.
- Threat Intelligence: Leverage threat intelligence feeds to stay informed about the latest threats and vulnerabilities and proactively update security policies.
- Regular Security Assessments: Conduct regular security assessments and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities and improve security posture.
User Education and Training
- Security Awareness Training: Educate users about security best practices, such as recognizing phishing attacks, using strong passwords, and reporting suspicious activity.
- Zero Trust Principles: Train employees on the principles of Zero Trust and how it applies to their daily work.

The Dispersive Zero Trust Academy provides expert insights, best practices, and real-world applications to help your organization strengthen its security posture. Want to dive deeper? Check out our Preemptive Cyber Defense White Paper for in-depth strategies and real-world solutions.
